What is Overpronation? Find Out How Insoles Can Help

You might not have heard of Overpronation, but it can cause orthotic insoles to be necessary for certain people. Knowing what Overpronation means is tough enough, but knowing the cause and how to fix it is even tougher.
The first thing that many people don’t know about Overpronation is that it’s not just something that happens in runners; a lot of non-runners experience it too.
Here are some of the basics surrounding Overpronation:
Properly aligning your foot during the course of a walk or run can reduce pain and other medical problems, including arch collapse. This is often accomplished with shoe inserts that correct Overpronation by only profiting medial-compressed feet, not by correcting general alignment.
Installing a high-quality insole into your footwear can improve Overpronation and provide better alignment. A quality insole should have an arch which is the same as your feet, to help with pain relief.
What is Overpronation?
In everyday life, we walk and run upright on hard surfaces, which causes the foot to supinate (instead of pronate) slightly.
Overpronation occurs when one or both feet roll inward excessively during these steps – about 60% of people have this motion more than they need to in order to function properly.Overpronation often happens when the foot rolls inward before pushing off, and when this occurs at different points of stride there is a loss of efficiency in every step taken.
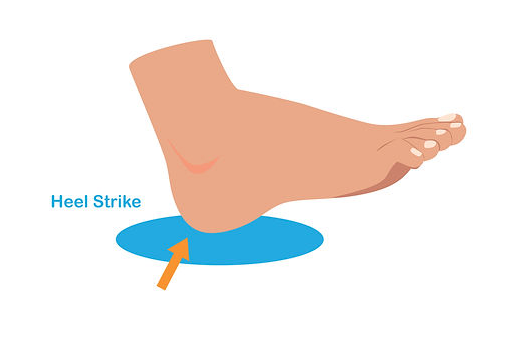
Basic Foot Biomechanics
To understand Overpronation, you need to know what happens to your foot when you take a step. We have broken down the process step-by-step:
- The heel strike is on the outside of your heel.
- Your foot rolls inwards, towards the toes. The body weight starts at the heel and goes over to the outside of your foot before moving forward.
- When you overpronate, your feet roll inward. This makes it less likely for shock to be distributed efficiently and can lead to back and foot pain. A good pair of shoes with insoles are designed to help absorb this excess force so that the foot is more stable as it hits the ground.
- When your foot moves, your ankle, knee and hip also turn.
- Push-off should happen when your second toe is on the ground behind you.
- It is not good if you keep your feet inside of your shoes. This is Overpronation.
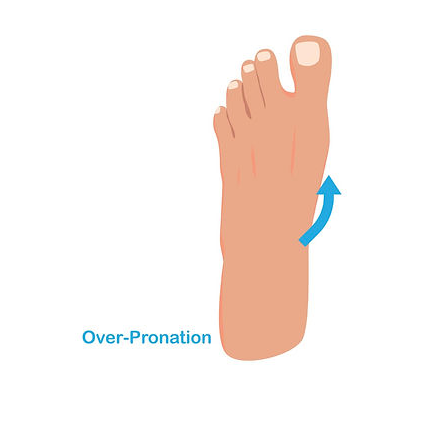
Overpronation
Overpronation is when your foot flattens, your toes turn outwards and the surrounding muscles are overworked.
- The arch of your foot is important. If the arch flattens, it puts pressure on the heel and causes fatigue. It also makes your foot slide forward in your shoe.
- When the toes point outward, it is no longer stable. You can’t walk forward as well when your toes are turned out.
- The inward roll of the ankle, knee and hip can cause you to feel pain. Especially if you are on your feet all day.
One way to reduce Overpronation, which can lead to excessive wear on joints and muscles, is with motion control shoes. Support under the calcaneal shelf will help you maintain a more even stride for efficient running and enjoyable walking.
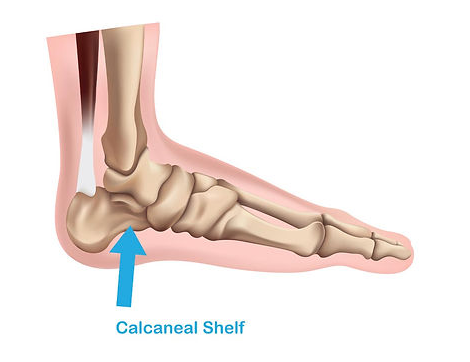
How to tell if you are an overpronator
Pronation is not always obvious- most people take their way of walking and running for granted. You can always consult with a foot and ankle specialist to figure out if you have this common condition, but there are ways you can tell at home as well.
Knowing your arch height helps figure out if you are Overpronation. If you have a flat foot and flexible arches, then you are an overpronator. First, it’s important to know if the shoes you’re wearing for running or walking contribute to your pronation or provide relief. You can easily check this by looking at the arches of the shoe.
The negative effects of Overpronation.
If you overpronate, there are a few different problems that can develop. They range from minor to uncomfortable and include:
Arch Collapse – When your arch collapses, your foot slides forward in your shoe. This can lead to contact with the inside of the shoe and cause problems like friction and blistering. When you hike, this can cause toes to hit shoes or socks and that can make black toe nails happen as well as making it uncomfortable.
Plantar Fasciitis – Constant elongation of the arch in your feet puts stress on your plantar fascia, a connective tissue located at the bottom of your foot.
Inefficiency – can be damaging to your joints. Upsets in alignment cause an imbalance, which can lead to injuries in those areas
Pain in the Kinetic Chain – A kinetic chain is a series of joints affected by one motion. Rolling your foot can twist other joints like your ankle, knee, and hip. They might not work as well because this happens. Then you feel pain or overuse injuries.
How do I correct Overpronation?
To correct Overpronation, you may need to use a shoe with lots of support. This is easier than it sounds. You can also find the right pair of shoes for your needs easily. You can also get insoles that will help your feet with this problem if needed.Not so long ago, the primary goal of a running shoe was to maximize overcorrections in stride for excessive pronators but now running shoes have shifted to improving comfort and reducing injury.
What are the best Overpronation insoles?
Pronation is the inward movement of the foot from a straight position. Firm arch support, whether it be custom orthotics or non-prescription insoles can help with alignment.
You have two choices to consider – get custom orthotics or purchase Overpronation orthotic insoles. Take a look at the circumstances that might make one option better than the other:
- Custom orthotics – are usually necessary only if you have complicated clinical symptoms.
- Non-prescription insoles – When you buy insoles, beware of over-the-counter options. Some don’t provide enough support for your feet and they can be uncomfortable and ineffective.
Overpronation is a common condition that occurs when the foot rolls inwards too far, which can cause pain and instability. Custom orthotics or insoles are often prescribed to correct Overpronation because they redistribute pressure evenly underfoot, providing comfort for your feet while also reducing shock-load on other parts of the body such as knees and back.